The WWW has now existed for three decades now. It has become the backbone of our communications and work life. Right now, millions of users use the web, while creating value for the economy and the growth of human society towards new horizons. However, the web is changing at a fast pace and at this stage, we are moving towards a decentralized web known as Web 3.0.
But, before we get into the topic, let’s review the history of Web 1.0 and Web 2.0.
What is the Web?
The web is a network of interconnected systems, including hosts and users. Tim Berners-Lee created it in 1989. He was kind enough to allow others to use it freely and did not file a patent for it. Web 1.0 is the current name for what came into existence back in the early 90s.
Web 1.0 (1990-2000)
The original World Wide Web consisted of static websites created with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. There weren’t many web applications on the internet and communications were mostly one-way.

Web 2.0 (2000-2010)
Web 2.0 took a significant step away from Web 1.0. Visual design gained importance but interactivity became a key aspect of the Internet. Web 2.0 saw the rise of several popular media consumption platforms such as Wikipedia, YouTube, Flickr, and Facebook, where all the content is created by the users. The lines between content creators and consumers began to blur.
At the same time, the first signs of information overload appeared. The number of Internet users increased from 738 million to 3.2 billion in under a decade.
Today: Web 3.0 (2010 - …)
Web 3.0 takes the web experience one step further by focusing on the human aspect. Platforms are becoming more inclined towards customizing our experience and protecting our privacy.
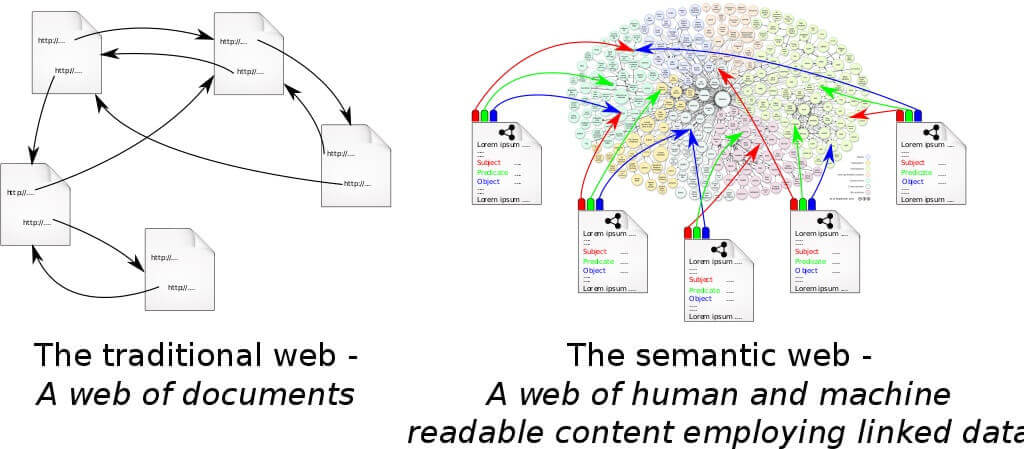
This new version of the Internet is closely linked to the concept of ‘Semantic Web’, which, in general terms, seeks to introduce a series of languages and procedures that can interpret user characteristics in order to offer a more personalized experience.
Definition of Web 3.0
Web 3.0 is an extended Web, endowed with greater meaning, in which any user on the Internet will be able to find answers to their questions in a faster and easier way thanks to better defined information about what they are looking for.
With the evolution of technologies such as Artificial Intelligence and Big Data, it is easier than ever to provide a personal and individual web experience.
Web 3.0 and A.I.
On top of this, Web 3.0 will be optimized from a semantic point of view. The “semantic web” allows data to be shared across multiple systems, platforms and users. In this framework, we can interact with the network through a natural language, interpreted by the software. Accessing information becomes much easier. In other words, all data hosted on web 3.0 should be “understood” by machines, which could process it quickly.
The web 3.0 is related to artificial intelligence. The websites would even have the ability to connect with each other according to the interests of the user.
What’s New on the Web 3.0?
Smart searches
Web 3.0 aims to create a new webpage taxonomy linked to the needs and characteristics of individual users. In this way, by connecting to the Internet, users can enjoy a much more personalized and useful platform.
Evolved social media
Social communities are growing online, both in number and in level of complexity. The ways of connecting to these networks are also increasing. For example, the “metaverse” will continue to grow. These are virtual-reality spaces in which users can interact with a virtual environment and other users.
Geospatial and 3D spaces
We have new ways of viewing the web, including three-dimensional spaces and augmented-reality-based environments, based on the user’s geographic location.
Decentralization
Currently the web has a hierarchical and centralized organization, but with the emergence of distributed ledger technologies like the blockchain, user data can be decentralized and more secure.
With a decentralized infrastructure, Web 3.0 will allow the creation of peer-to-peer connections (P2P), which can potentially reduce the power of large technology companies that monopolize and profit from user data.
A faster web
The new features of Web 3.0 require a much faster Internet. In response to this, the main telecommunications operators have implemented broadband connections to guarantee a more satisfactory user experience for users.
Cloud computing
With the creation of new storage spaces, not only for data but also for programs, the web becomes an executable space like a universal computer. Like an Internet Operating System, the user interface allows people to access applications not stored on their computers but completely or partly on Internet.
Multiple devices
We use more and more devices and very different from each other. We are not only talking about a computer and a mobile phone, but also about other devices such as tablets, televisions, electronic books … From many computers we will be able to navigate and use different services that are part of our day to day. Thanks to this greater accessibility, we can easily achieve it without complications when using a different device.
In Conclusion
In the three decades of the web’s life, the importance of the Internet has grown exponentially. Its presence has increased dramatically and has taken over more spaces each time. We don’t know what the future holds but the WWW seems to be growing towards a space where the boundaries between machines and people are becoming less visible than ever.



